Anushka Super Speciality Eye Hospital
Call: 90044 44422 / 99213 44422 | Timings : 8.30 a.m to 5.30 p.m (Mon-Sat) | Add: Shri Swami Samarth Soc, Kaneri Dhamankar Naka, Bhiwandi




Accredited for Quality Care
Retinal Detachment: Causes, Symptoms, Types, Treatment, and Complications
anushka
22 August 2025
Introduction to Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a serious eye emergency in which the retina — the thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye — separates from its underlying supportive tissue.
This separation prevents the retina from functioning properly, leading to sudden vision loss if not treated promptly. Retinal detachment is painless but can cause permanent blindness if not addressed immediately.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, retinal detachment affects about 1 in 10,000 people per year, most often in middle-aged or older adults, though it can occur at any age.
What Causes Retinal Detachment?
The retina is nourished by a network of blood vessels and supported by the vitreous gel. Retinal detachment usually happens when a tear or hole allows fluid to pass underneath the retina, separating it from the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
Common Causes and Risk Factors
- Aging changes – vitreous gel shrinks and pulls away from retina
- Retinal tears or holes – often from posterior vitreous detachment
- Eye injury or trauma
- Previous eye surgery – especially cataract removal
- Extreme myopia (high short-sightedness)
- Family history of retinal detachment
- Inflammatory eye diseases
Diabetic retinopathy – new blood vessels can cause traction
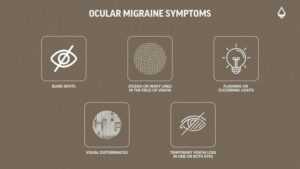
Signs and Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is painless, but symptoms appear suddenly and may progress quickly.
Warning Signs:
- Sudden appearance of floaters (black spots, threads, cobweb-like shapes)
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Shadow or curtain-like darkness spreading across the field of vision
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Sudden decrease in visual clarity
Pro Tip: If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention — early treatment greatly improves outcomes.
Types of Retinal Detachment
1. Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
- Most common type
- Caused by a tear or hole in the retina
- Fluid from vitreous space passes through tear, lifting retina away
2. Tractional Retinal Detachment
- Caused by scar tissue pulling on the retina
- Often occurs in people with diabetic retinopathy
3. Exudative (Serous) Retinal Detachment
- No tear present
- Caused by fluid buildup beneath retina due to inflammation, injury, or tumors
Stages and Progression
- Initial tear or hole – often symptom-free until vitreous fluid enters
- Partial detachment – early intervention possible
- Total detachment – rapid vision loss, urgent surgery needed
How is Retinal Detachment Diagnosed?
An ophthalmologist performs a detailed eye exam using:
- Dilated fundus examination – direct view of retina
- Ophthalmoscopy – checks for tears, holes, and detachment
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) – detailed retina images
- Ultrasound scanning – if bleeding obscures retina
Treatment for Retinal Detachment
Goal: Reattach the retina and seal any tears to prevent fluid leakage.
1. Laser Photocoagulation
- Uses laser to create burns around the tear
- Seals retina to underlying tissue
- Effective for small tears and holes before detachment
2. Cryopexy (Freezing Treatment)
- Freezing probe applied to outer eye wall
- Creates scar tissue sealing the tear
- Often combined with other procedures
3. Pneumatic Retinopexy
- Gas bubble injected into vitreous cavity
- Patient positions head to allow bubble to push retina back
- Combined with laser or cryopexy to seal tear
4. Scleral Buckling Surgery
- Silicone band placed around eye to press wall inward
- Reduces vitreous traction and supports retinal healing
- Used for large or complex detachments
5. Vitrectomy
- Removes vitreous gel pulling on retina
- Replaces gel with saline, gas, or silicone oil
- Often used in tractional or severe cases
Possible Complications of Retinal Detachment
Without prompt treatment:
- Permanent vision loss
- Blindness in affected eye
- Macular damage – loss of central vision
- Glaucoma – due to increased pressure
- Recurrent retinal detachment
- Infection or bleeding after surgery
Recovery After Surgery
- Vision improvement may take weeks to months
- Gas bubble requires avoiding air travel until absorbed
- Eye drops prescribed to prevent infection and inflammation
- Regular follow-up visits essential
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities during healing
Prevention Tips
While not all detachments are preventable:
- Regular eye exams – especially for high-risk groups
- Protect eyes from injury
- Manage diabetes and other systemic conditions
- Seek urgent care for sudden flashes, floaters, or vision changes
- Follow-up after cataract surgery or severe eye trauma
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is retinal detachment painful?
No, it’s painless, but vision changes are sudden and alarming.
Q2. Can retinal detachment heal on its own?
No—surgery is required to reattach the retina.
Q3. How quickly should I get treatment?
Immediately—delaying treatment increases the risk of permanent blindness.
Q4. Will my vision return to normal after surgery?
It depends on the extent of detachment and if the macula was involved. Early treatment improves chances.
Q5. Can both eyes be affected?
Yes—if one eye has had a detachment, the other is at higher risk.
Q6. How long is recovery after surgery?
Most people recover in 2–6 weeks, but full vision improvement may take months.
Q7. Who is most at risk?
People with high myopia, history of eye injury, previous retinal detachment, or diabetic eye disease.
Conclusion
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency that can cause irreversible blindness if not treated quickly. Recognizing early warning signs like sudden floaters, flashes, or vision shadows can save your sight.
With modern surgical techniques, most cases can be successfully repaired — but early diagnosis is critical. Regular eye check-ups, especially if you are in a high-risk group, can make the difference between saving or losing vision.
Why Nutrition Matters for Eye Health?
Recent Posts